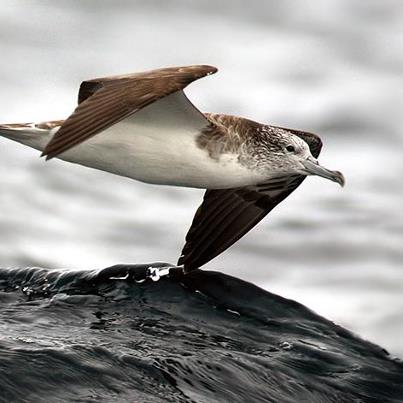
Susan Rehorek (Department of Biology, Slippery Rock University, Slippery Rock, Pennsylvania, USA) and colleagues have published in the Journal of Morphology on the morphology of developing eggs of the Laysan albatross Phoebastria immutabilis.
The paper’s abstract follows:
“Bird incubation is subdivided into two phases: differentiation (embryonic phase) and growth (fetal phase). Most birds have a relatively short incubation period (20–30 days) with the phase transition occurring midway through the incubation period. The Laysan albatross (Phoebastris [sic] immutabilis) is a large pelagic bird with a long incubation period. The purpose of this study was to document the differentiation phase with the aim of ascertaining the impact of a lengthened incubation on embryonic development. Eighty-two previously collected albatross embryos were examined, measured, and staged. The albatross was found to develop more slowly than smaller birds, with a rate similar to other long-incubating birds. Legs and wings grow at similar rates but exhibit variation in growth among their anatomical components. While the albatross embryos shared some morphological stages with chickens, they were more similar to ducks and pelicans. Special features of the albatross not shared with the Gallianserae (chickens and ducks) included an alligator-like curved tail, narial tubes, and a cloacal bulge. Further examination of other larger pelagic birds with long incubation periods are needed to determine the uniqueness of the Laysan albatross embryonic development. Although much embryonic phase growth was documented in the postnatal period, little is known about the later, fetal phase in Laysan albatross. Future studies should involve examination of later (post day 32) fetuses.”

Laysan Albatross egg, photograph by Pacific Rim Conservation
Reference:
Rehorek, S.J., Smith, T.D. & Beeching, S.C. 2016. Early development and differentiation of the Laysan albatross (Phoebastria immutabilis (Rothschild, 1893): Procellariiformes). Journal of Morphology DOI: 10.1002/jmor.20572.
John Cooper, ACAP Information Officer, 05 July 2016

 English
English  Français
Français  Español
Español 




