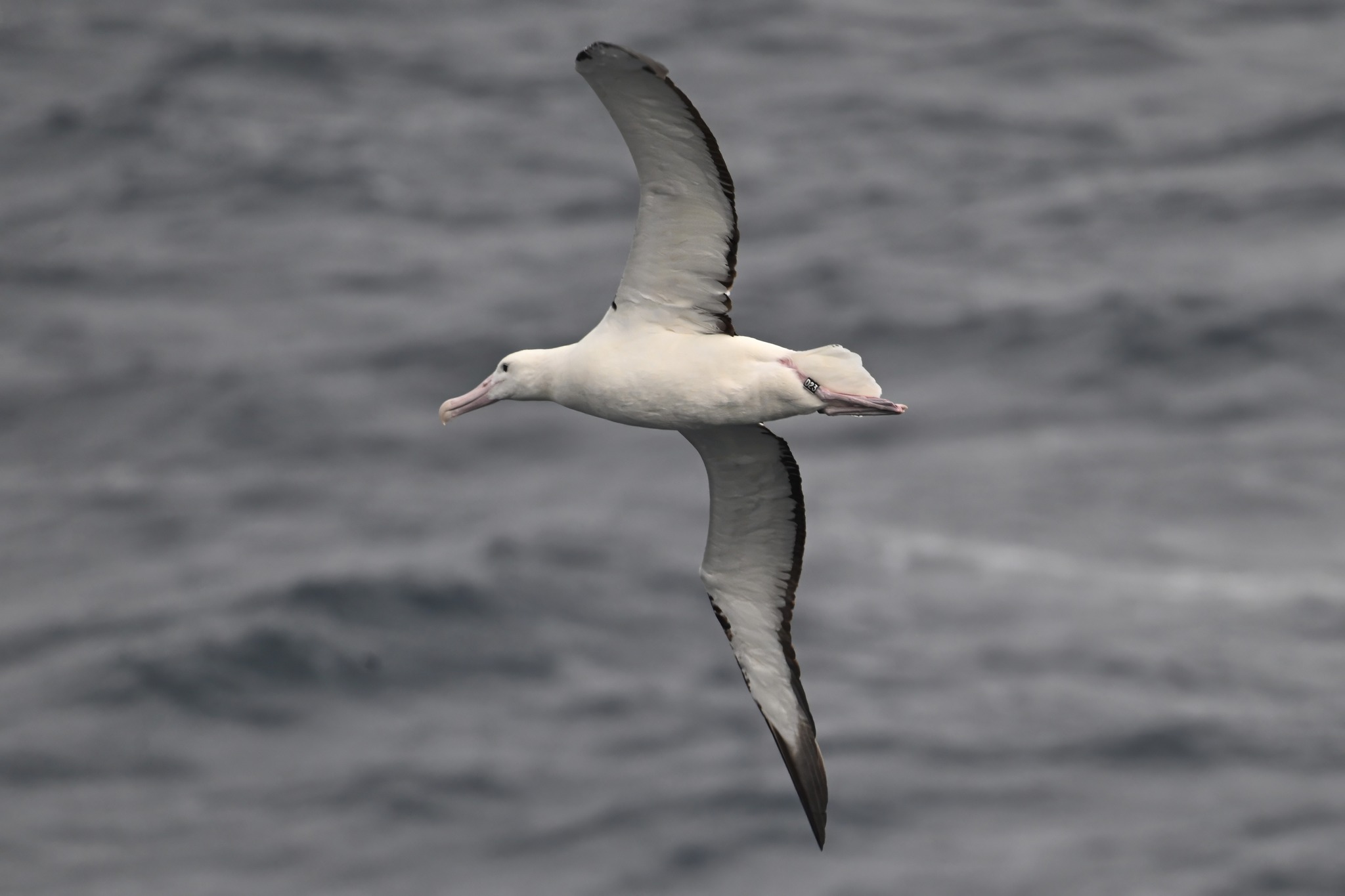
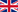
 D23 (band readable on expanding) in Chilean waters, photograph by Dan Mosher
D23 (band readable on expanding) in Chilean waters, photograph by Dan Mosher
Dan Mosher has reported on Facebook of photographing an Endangered Northern Royal Albatross Diomedea sanfordi off the coast of Chile. The bird carried a black plastic band on its left leg engraved with D23.
He writes “I recently returned from a cruise [aboard the] Oosterdam from San Antonio, Chile to the Antarctica Peninsula to Buenos Aires and back again. I’m a deck-watcher and enjoy seeing and photographing the pelagic seabirds we encounter along the way. On the return trip from Puerto Montt Chile going [north] toward San Antonio, we came across a tagged royal albatross that was quite close to the ship. The tag clearly reads D23”. He adds in a comment that the date was 21 February 2026.
Following enquiries posted to his page, the bird was confirmed to be a Northern Royal Albatross from the Taiaroa Head/Pukekura mainland colony near Dunedin in New Zealand, and that it is a male, hatched in 2023, one of 33 chicks to fledge from the colony that [2022/23] season.
Let’s hope it will return to the colony and eventually commence breeding.
John Cooper, Emeritus Information Officer, Agreement on the Conservation of Albatrosses and Petrels, 12 March 2026

 English
English  Français
Français  Español
Español  Big Ben on Heard Island, photograph by Barbara Wienecke
Big Ben on Heard Island, photograph by Barbara Wienecke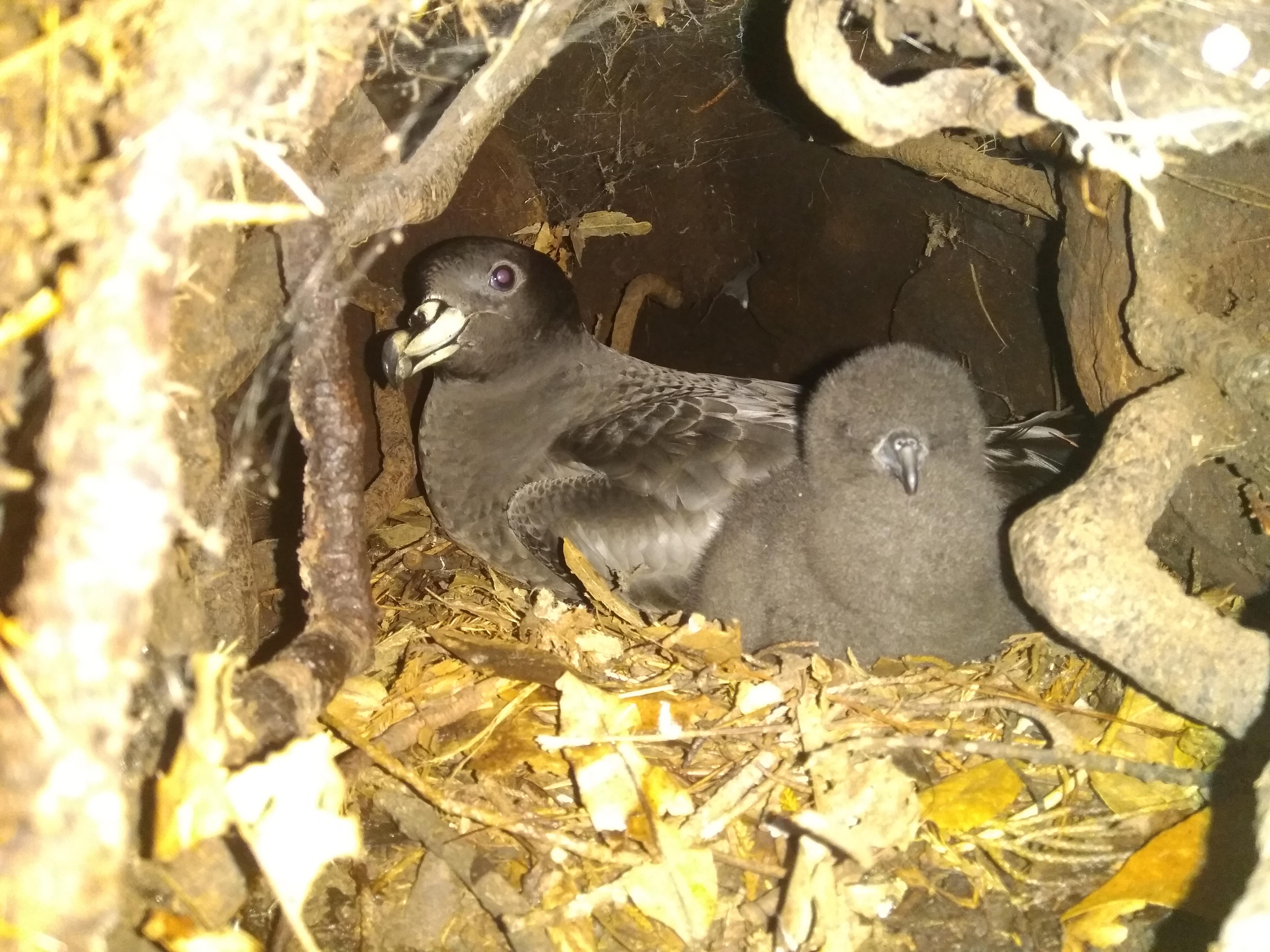 An adult Black Petrel with its downy chick, photograph by George Hobson
An adult Black Petrel with its downy chick, photograph by George Hobson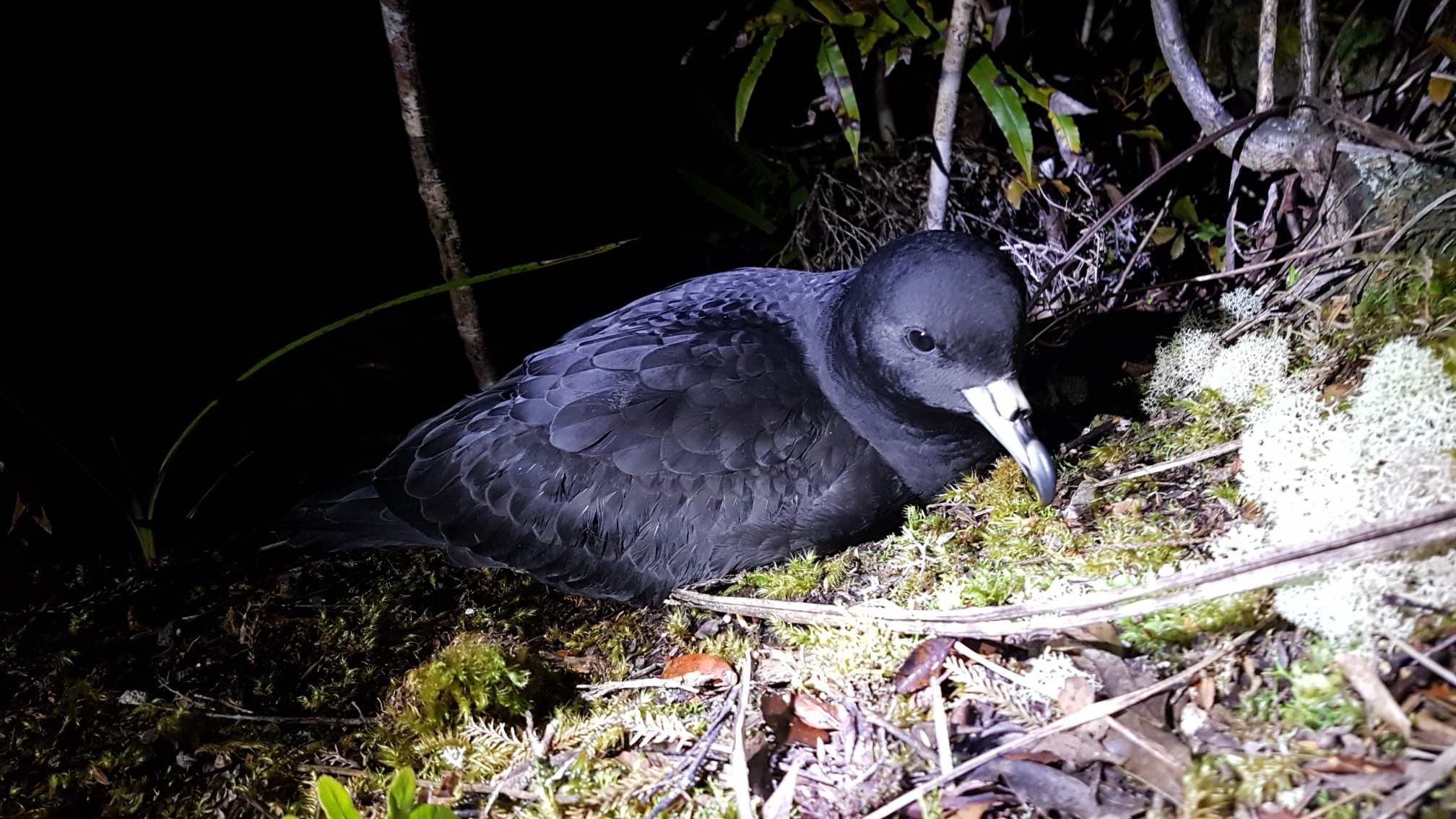 A
A 
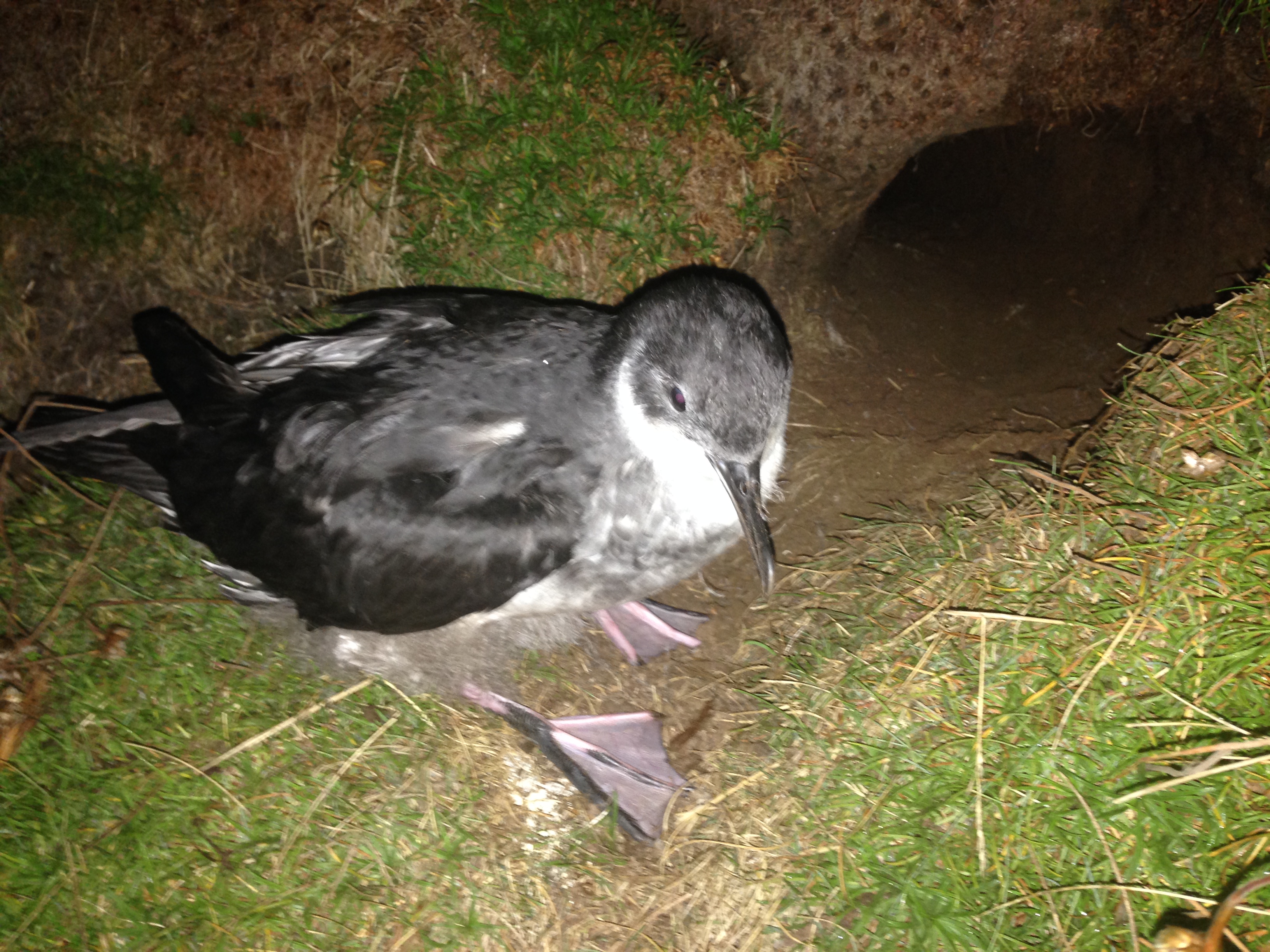 A Manx Shearwater chick outside its burrow, photograph by Jaclyn Pearson
A Manx Shearwater chick outside its burrow, photograph by Jaclyn Pearson