Alejandra Piro (División Zoología Vertebrados, Museo de La Plata, Argentina) and Carolina Acosta Hospitaleche have published in the journal Polar Biology on morphology of the skull of the Southern Giant Petrel Macronectes giganteus.
The paper’s abstract follows:
“The Southern Giant Petrel Macronectes giganteus is the largest Procellariidae around the world. Beyond the most striking features on the skull, the strong hooked bill with tubular, dorsally-placed, external nostrils, these petrels have been the focus of diverse studies, except osteological ones. Even less is known about the osteology in juveniles and chicks. A comparative description of the skull anatomy of the Southern Giant Petrel M. giganteus, highlighting the differences along each postnatal ontogenetic stage, is given here. As a result, we found that the shape of the skull does not vary among the compared stages and that there is a progression in the fusion of the elements of the skull and mandible. Besides, less obvious results show a little intraspecific variation among specimens of the same ontogenetic stage, involving osteological features such as the quantity and shape of foramina within pneumatic bone surfaces, and the fact that general size is not associated with sexual dimorphism. The beak acquires its characteristic development and sturdiness from early stages. Conversely, the fossae glandulae nasalis is only developed in juveniles and adults, being absent in earlier stages.”

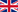
A white-phase Southern Giant Petrel on Bouvet Island, photograph by Greg Hofmeyr
Reference:
Piro, A. & Acosta Hospitaleche, C. 2018. Skull morphology and ontogenetic variation of the Southern Giant Petrel Macronectes giganteus (Aves: Procellariiformes). Polar Biology doi.org/10.1007/s00300-018-2397-z.
John Cooper, ACAP Information Officer, 15 October 2018

 English
English  Français
Français  Español
Español 



