Cerren Richards (Department of Ocean Sciences, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St John’s, Canada) and colleagues have published open access in the journal PeerJ on rafting by Manx Shearwaters Puffinus puffinus around the Welsh island of Skomer.
The paper’s abstract follows:
“Before visiting or leaving their remote island colonies, seabirds often engage in a behaviour termed ‘rafting’, where birds sit, often in groups, on the water close to the colony. Despite rafting being a widespread behaviour across many seabird taxa, the functional significance of rafting remains unknown. Here we combine global positioning system (GPS) tracks, observational and wind condition data to investigate correlates of rafting behaviour in Manx shearwaters (Puffinus puffinus) at a large colony on Skomer Island, Wales. We test (1) the influence of wind direction on rafting location and (2) whether raft size changes with respect to wind speed. Our approach further allows us to describe day-night trends in (3) raft distance from shore through time; (4) the number of birds present in the nearshore waters through time; and (5) spatial patterns of Manx shearwater rafts in marine waters adjacent to the breeding colony. We find no evidence that wind direction, for our study period, influences Manx shearwater rafting location, yet raft size marginally increases on windier days. We further find rafting birds closer to the shore at night than during the day. Thus, before sunset, birds form a “halo” around Skomer Island, but this halo disappears during the night as more individuals return from foraging trips and raft nearer the colony on Skomer Island. The halo pattern reforms before sunrise as rafts move away from land and birds leave for foraging. Our results suggest that wind conditions may not be as ecologically significant for rafting locations as previously suspected, but rafting behaviour may be especially important for avoiding predators and cleaning feathers.”

Manx Shearwater on the sea surface, photograph by Nathan Fletcher
Reference:
Richards, C., Padget, O., Guilford, T. & Bates, A.E. 2019. Manx shearwater (Puffinus puffinus) rafting behaviour revealed by GPS tracking and behavioural observations. PeerJ 7: e7863 doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7863.
John Cooper, ACAP Information Officer, 14 November 2019

 English
English  Français
Français  Español
Español 



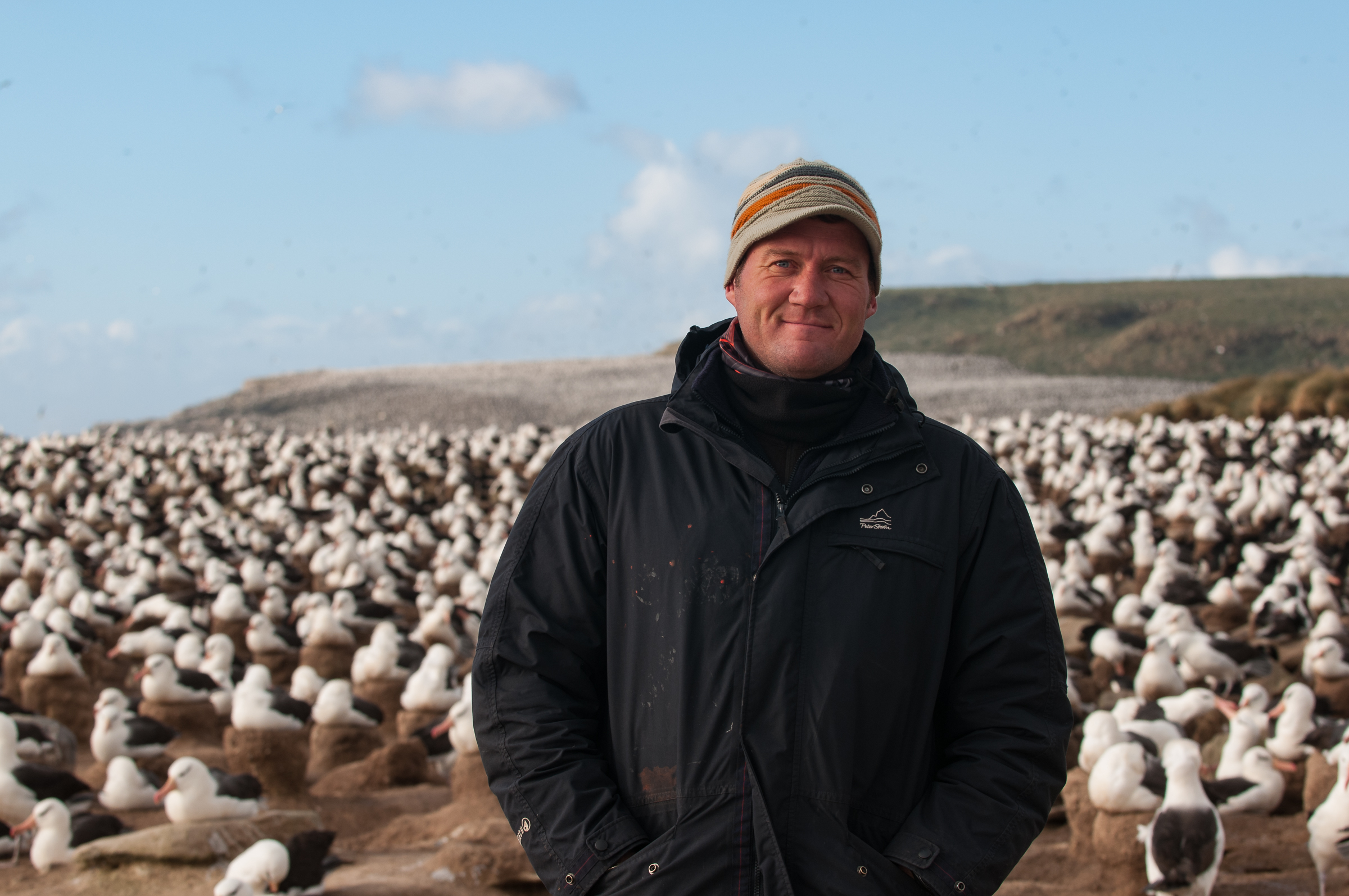
 Mark Tasker from the UK,
Mark Tasker from the UK, 

