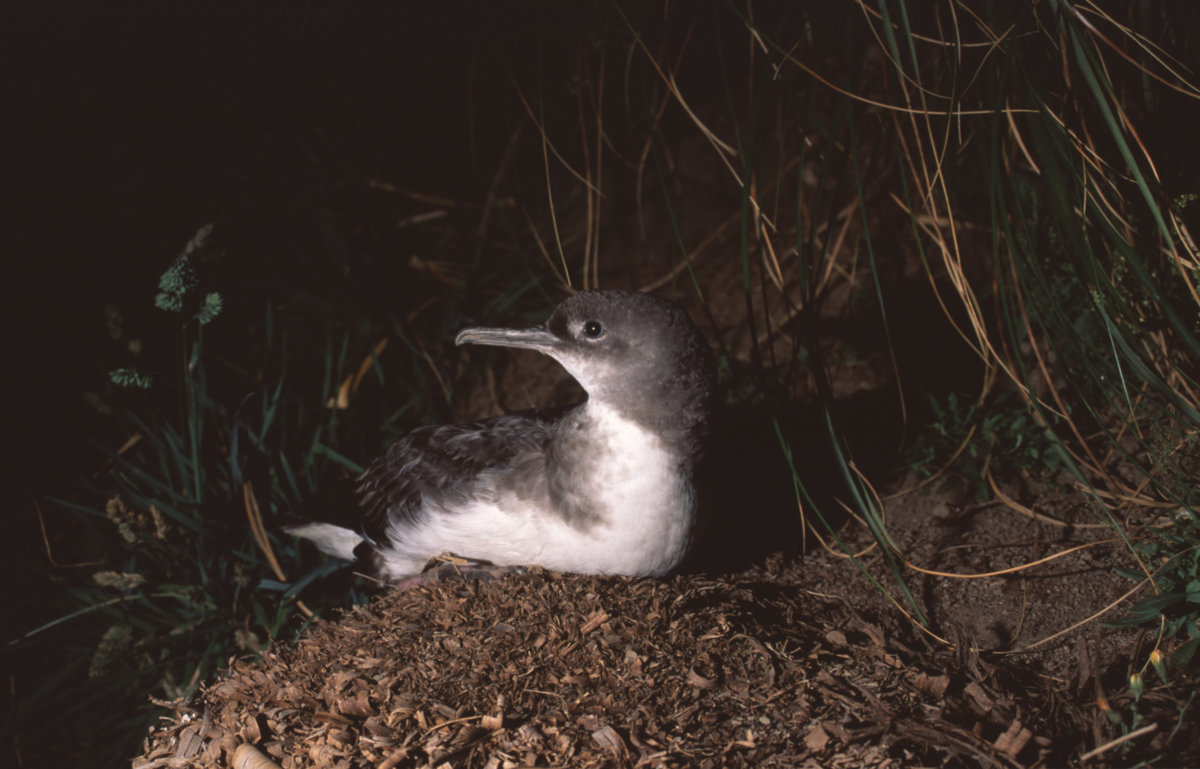
Globally Endangered Newell’s Shearwaters Puffinus newelli commenced breeding for the first time last year within the Makamakaole Stream fenced sanctuary on Hawaii’s Maui Island. The predator-free enclosures were established in 2013 to keep out feral cats, rats and mongooses.
“For the first time in four years, Newell’s shearwaters have started laying eggs in an artificially created seabird colony in West Maui. Biologists confirmed that four human-made burrow boxes - three with eggs - are being occupied by the threatened species this season”.
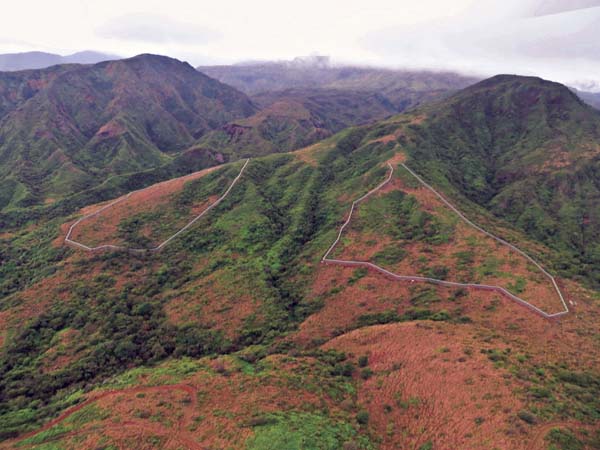

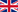
The two Makamakaole Stream fenced enclosures

Newell's Shearwaters at the entrance to an artificial burrow inside a Makamakaole Stream enclosure
Two predator-free enclosures were constructed near the Makamakaole Stream basin in 2012 and 2013 to offset accidental deaths of native seabirds by wind turbines at TerraForm Power’s Kaheawa wind energy facilities on Maui.

A Kaheawa wind farm on Maui
Photographs by TerraForm Power
Acoustic attraction has been used to attract prospecting shearwaters:
“Every night, seabird social calls similar to those at existing colonies were broadcast through weatherproof, solar-powered sound systems. Within the enclosures, biologists have installed 100 “burrow boxes.” The corrugated plastic burrows connect to underground plywood boxes that serve as nesting chambers, mimicking the birds’ own natural habitats. A 6-foot-high [1.8 m] mesh fence protects the enclosures, and “year-round intensive predator control” keeps the area clear of predators. The goal was to attract the shearwater and the endangered [in the USA] Hawaiian petrel to an area where both species had been assumed absent for more than a decade.”
Globally Vulnerable Hawaiian Petrels Pterodroma sandwichensis have "shown interest” but as yet have not bred within the enclosures.
“An estimated 16 [Hawaiian] petrels have been killed at the Kaheawa I site since it was permitted in 2006, and none at Kaheawa II since it was permitted in 2012, said Mitchell Craig, TerraForm’s compliance manager for its Habitat Conservation Plan. Biologists have not recorded any Newell’s shearwaters killed at either site. The total estimated take over the 20-year period is 31 petrels and zero shearwaters at Kaheawa I, and neither petrels nor shearwaters at Kaheawa II.”
Read more here.
John Cooper, ACAP Information Officer, 10 January 2018

 English
English  Français
Français  Español
Español 





