Fernanda Colabuono (Universidade de São Paulo, Instituto Oceanográfico, Laboratório de Química Orgânica Marinha, São Paulo, Brazil) and colleagues have published in the journal Environmental Pollution on persistent organic pollutants in Southern Giant Petrel Macronectes giganteus from the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica.
The paper’s abstract follows:
“Seabirds play an important role as top consumers in the food web and can be used as biomonitors of exposure to pollutants. Contamination studies involving non-destructive sampling methods are of considerable importance, allowing better evaluation of the levels of pollutants and their toxic effects. In the present study, organohalogen contaminants were analyzed in 113 blood samples from Southern Giant Petrel (Macronectes giganteus) adults and chicks collected in the austral summer of 2011/2012 and 2012/2013 from colonies on Elephant and Livingston Islands, South Shetland, Antarctica. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), hexachlorobenzene (HCB), pentachlorobenzene (PeCB), mirex, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroetane and derivatives (DDTs) and chlordanes were detected in all birds, whereas polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) were not detected in any blood samples. No significant differences were found in organochlorine levels between sampling events. Adults exhibited significantly higher levels than chicks, except for PeCB. PCBs, HCB, mirex and DDTs were statistically similar in males and females from Elephant Island. Females on Livingston Island exhibited higher HCB values than males, but no sex differences were found regarding other organochlorines. The similarity in organochlorine levels between sexes in birds with very marked sexual segregation in feeding habits during the breeding season may indicate that significant amounts of contaminants are acquired during migration to lower latitudes, when the diets of males and females are similar. Birds sampled on Livingston Island exhibited significantly lower levels of PCBs, HCB, DDTs, mirex and chlordanes in comparison to those on Elephant Island, which could be the result of distinct foraging patterns between the two colonies. Organochlorine levels were similar between years in birds captured in two consecutive breeding seasons. Blood samples from Southern Giant Petrels adults and chicks proved to be useful for the comparison of intraspecific contamination levels and appear to be adequate for the long-term assessment of organohalogen contaminants in antarctic top predators.
Organochlorine contaminants in blood samples of Southern Giant Petrels reflected intra-specific differences and suggested distinct foraging patterns between colonies.”

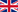
A white-phase Southern Giant Petrel in Antarctica, photograph by Michael Dunn
Click here for a related paper by Fernanda Colabuono.
Reference:
Colabuono, F.I., Vander Pol, S.S., Huncik, K.H., Taniguchi, S., Petry M.V., Kucklick, J.R. & Montone, R.C. 2016. Persistent organic pollutants in blood samples of Southern Giant Petrels (Macronectes giganteus) from the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Environmental Pollution 216: 38-45.
John Cooper, ACAP Information Officer, 13 June 2016

 English
English  Français
Français  Español
Español