Ewan Wakefield, Richard Phillips and Mark Belchier (British Antarctic Survey, Cambridge, UK) writing in the journal Antarctic Science have shown that bottom topography is important for where Black-browed Albatrosses Thalassarche melanophris choose to forage.
The paper's abstract follows:
"Wide-ranging, surface-feeding pelagic seabirds are the most numerous functional group of birds in the Southern Ocean. The mesoscale habitat use of these birds is increasingly being quantified by relating their movements to remotely sensed, near surface properties of the ocean. However, prey availability at the sea surface may also be determined by habitat characteristics not measurable from space. For instance, benthic-pelagic coupling, which occurs when seabed processes affect productivity in the epipelagic zone, can link benthic habitat type to availability of surface prey. We combined acoustically derived maps of the substrate of the South Georgia shelf with GPS tracking to quantify the sub-mesoscale habitat use of breeding black-browed albatrosses. We show that albatrosses preferentially used waters overlaying glacial moraine banks near the shelf edge and that this was unrelated to the presence of trawlers targeting mackerel icefish, which are also associated with these features. Stomach temperature profiles suggest that albatrosses primarily caught krill and fish over the banks. We hypothesize that black-browed albatrosses target waters overlaying moraine banks due to upward benthic-pelagic coupling, mediated by an increase in abundance of zooplankton such as Antarctic krill. Our finding suggest that the potential effects of such processes on pelagic seabird distribution warrant wider investigation."
\
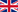
Black-browed Albatross at sea. Photograph by Luke Finley
Reference:
Wakefield, E.D., Phillips, R.A. & Belchier, M. 2012. Foraging black-browed albatrosses target waters overlaying moraine banks - a consequence of upward benthic-pelagic coupling? Antarctic Science DOI:10.1017/S0954102012000132.
John Cooper, ACAP Information Officer, 2 April 2012

 English
English  Français
Français  Español
Español