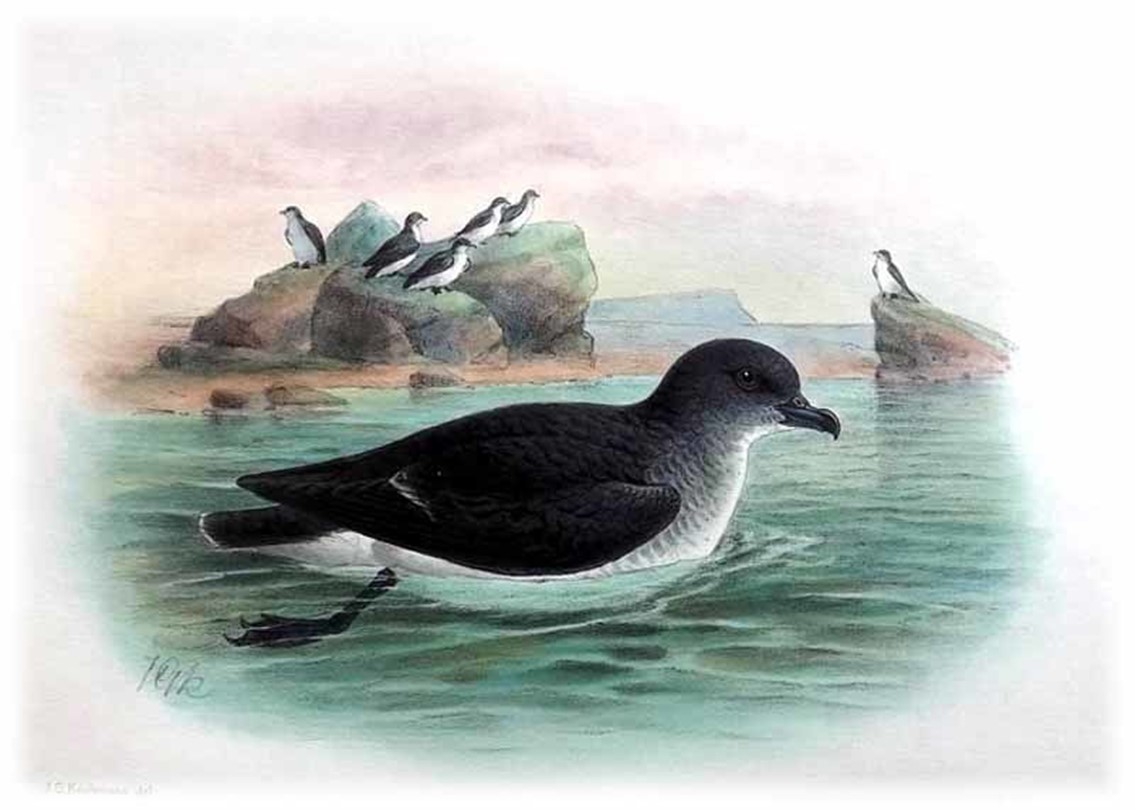

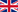
Common Diving Petrel, by Johannes Gerardus Keulemans, 1842-1912
Aymeric Fromant (School of Life and Environmental Sciences, Deakin University, Burwood, Australia) and colleagues have published open access in the journal Oecologia on niche segregation in the Common Pelecanoides urinatrix and the South Georgian P. georgicus Diving Petrels.
The paper’s abstract follows:
“Niche theory predicts that to reduce competition for the same resource, sympatric ecologically similar species should exploit divergent niches and segregate in one or more dimensions. Seasonal variations in environmental conditions and energy requirements can influence the mechanisms and the degree of niche segregation. However, studies have overlooked the multi-dimensional aspect of niche segregation over the whole annual cycle, and key facets of species co-existence still remain ambiguous. The present study provides insights into the niche use and partitioning of two morphologically and ecologically similar seabirds, the common (CDP, Pelecanoides urinatrix) and the South Georgian diving petrel (SGDP, Pelecanoides georgicus). Using phenology, at-sea distribution, diving behavior and isotopic data (during the incubation, chick-rearing and non-breeding periods), we show that the degree of partitioning was highly stage-dependent. During the breeding season, the greater niche segregation during chick-rearing than incubation supported the hypothesis that resource partitioning increases during energetically demanding periods. During the post breeding period, while species-specific latitudinal differences were expected (species specific water mass preference), CDP and SGDP also migrated in divergent directions. This segregation in migration area may not be only a response to the selective pressure arising from competition avoidance between sympatric species, but instead, could reflect past evolutionary divergence. Such stage-dependent and context-dependent niche segregation demonstrates the importance of integrative approaches combining techniques from different fields, throughout the entire annual cycle, to better understand the co-existence of ecologically similar species. This is particularly relevant in order to fully understand the short and long-term effects of ongoing environmental changes on species distributions and communities.
This work demonstrates the need of integrative multi-dimensional approaches combining concepts and techniques from different fields to understand the mechanism and causal factors of niche segregation.”
Reference:
Fromant, A., Arnould, J.P.Y., Delord, K., Sutton G.J., Carravieri, A., Bustamante, P., Miskelly, C.M., Kato, A., Braut-Favrou, M., Cherel, Y. & Bost, C.-A. 2022. Stage-dependent niche segregation: insights from a multi-dimensional approach of two sympatric sibling seabirds. Oecologia 199: 537-548.
John Cooper, ACAP Information Officer, 01 August 2022
Editorial Note: ACAP Latest News usually restricts its news posts to matters pertaining to the biology and conservation of the 31 species of ACAP-listed albatrosses and petrels and those procellariiform genera of particular interest to the Agreement, mainly gadfly petrels Pterodroma spp. and shearwaters Ardenna, Calonectris and Puffinus spp. In the case of the post above, diving petrels Pelecanoides spp. are not usually featured in ALN but the topic of niche segregation should be of interest and relevance to those studying closely related and sympatric species of ACAP-listed birds, such as the mollymawk albatrosses Thalasssarche and the giant petrels Macronectes spp.

 English
English  Français
Français  Español
Español