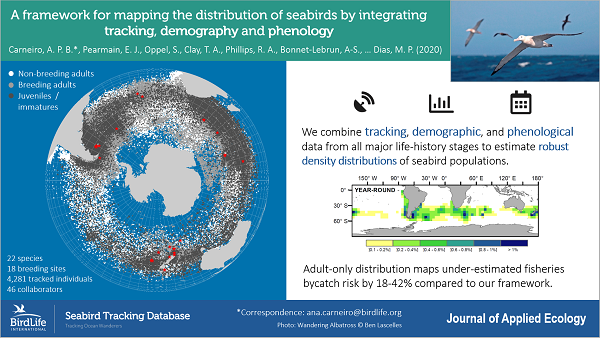
Ana Carneiro (BirdLife International, Cambridge, UK) and colleagues have published open access in the Journal of Applied Ecology on new developments in mapping the distribution of Southern Ocean seabirds.
The paper’s abstract follows
“1. The identification of geographic areas where the densities of animals are highest across their annual cycles is a crucial step in conservation planning. In marine environments, however, it can be particularly difficult to map the distribution of species, and the methods used are usually biased towards adults, neglecting the distribution of other life-history stages even though they can represent a substantial proportion of the total population.
2. Here we develop a methodological framework for estimating population-level density distributions of seabirds, integrating tracking data across the main life-history stages (adult breeders and non-breeders, juveniles and immatures). We incorporate demographic information (adult and juvenile/immature survival, breeding frequency and success, age at first breeding) and phenological data (average timing of breeding and migration) to weight distribution maps according to the proportion of the population represented by each life-history stage.
3. We demonstrate the utility of this framework by applying it to 22 species of albatrosses and petrels that are of conservation concern due to interactions with fisheries. Because juveniles, immatures and non-breeding adults account for 47–81% of all individuals of the populations analysed, ignoring the distributions of birds in these stages leads to biased estimates of overlap with threats, and may misdirect management and conservation efforts. Population-level distribution maps using only adult distributions underestimated exposure to longline fishing effort by 18–42%, compared with overlap scores based on data from all life-history stages.
4. Synthesis and applications. Our framework synthesizes and improves on previous approaches to estimate seabird densities at sea, is applicable for data-poor situations, and provides a standard and repeatable method that can be easily updated as new tracking and demographic data become available. We provide scripts in the R language and a Shiny app to facilitate future applications of our approach. We recommend that where sufficient tracking data are available, this framework be used to assess overlap of seabirds with at-sea threats such as overharvesting, fisheries bycatch, shipping, offshore industry and pollutants. Based on such an analysis, conservation interventions could be directed towards areas where they have the greatest impact on populations.”
With thanks to Richard Phillips, British Antarctic Survey.
Reference:
Carneiro, A.P.B., Pearman, E.J., Oppel, S., Clay, T.A., Phillips, R.A., Bonnet-Lebrun, A.-S. et al. 2020. A framework for mapping the distribution of Southern Ocean seabirds across life-history stages, by integrating tracking, demography and phenology. Journal of Applied Ecology doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.13568.
John Cooper, ACAP Information Officer, 06 February 2020

 English
English  Français
Français  Español
Español