Robson Santos (Departamento de Oceanografia e Ecologia, Universidade Federal do Espírito Santo, Vitória, Brazil) and colleagues have published in the journal Environmental Pollution on ingestion of plastic by marine animals including shearwaters Ardenna and Puffinus spp.
The paper’s abstract follows:
“In recent years marine plastic pollution has gained considerable attention as a significant threat to marine animals. Despite the abundant literature related to marine debris ingestion, only a few studies attempted to understand the factors involved in debris ingestion. Plastic ingestion is commonly attributed to visual similarities of plastic fragments to animal's prey items, such as plastic bags and jellyfish. However, this simple explanation is not always coherent with the variety of debris items ingested and with the species' main prey items. We assess differences in the conspicuousness of plastic debris related to their color using Thayer's law to infer the likelihood that visual foragers detect plastic fragments. We hypothesize that marine animals that perceive floating plastic from below should preferentially ingest dark plastic fragments, whereas animals that perceive floating plastic from above should select for paler plastic fragments.”
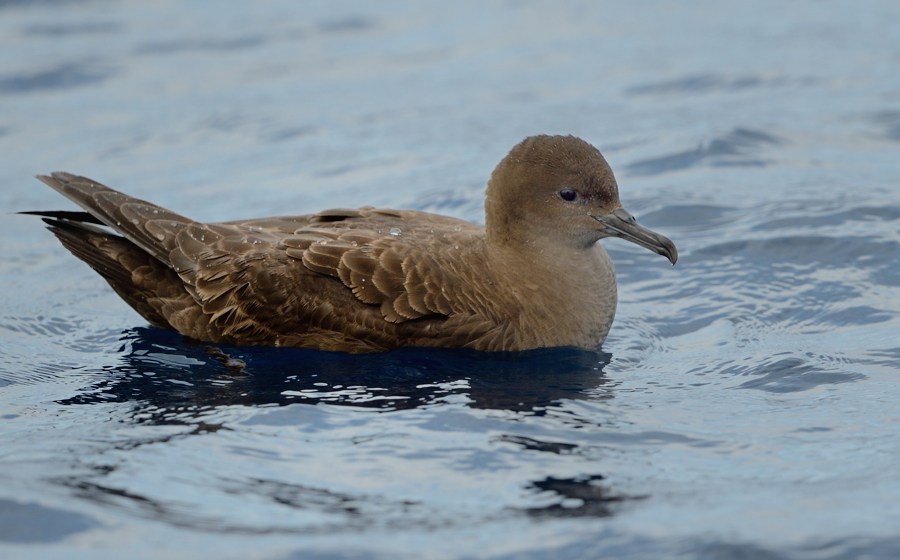

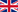
Short-tailed Shearwater at sea, photograph by Kirk Zufelt
Reference:
Santos, R.G., Andrades, R.,Fardim, L.M. & Martins, A.S. 2016. Marine debris ingestion and Thayer's law – The importance of plastic color. Environmental Pollution 214: 585-588.
John Cooper, ACAP Information Officer, 26 August 2016

 English
English  Français
Français  Español
Español